Herniated disc
What is a herniated disc?
If an intervertebral disc is no longer sufficiently resistant, its outer edge bulges and a disc protrusion (bulging) occurs. This often causes symptoms such as back pain and muscle tension. If part of the intervertebral disc breaks away from the intervertebral disc mass and protrudes out of the space between the vertebral bodies into the nerve canal, feelings of numbness or even paralysis may occur in the legs or arms.
A herniated disc, also known as a slipped disc, is treated conservatively or via a surgical intervention in the form of an operation.
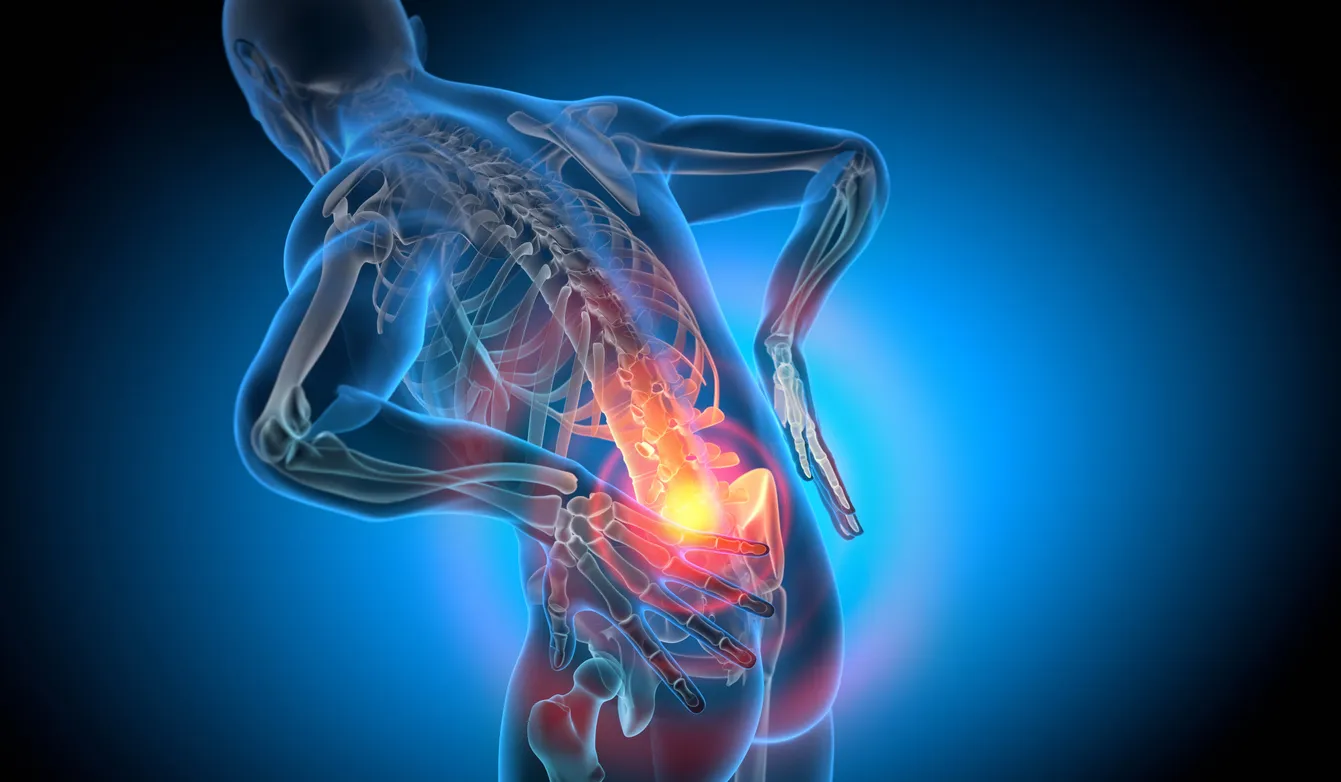
If you have a herniated disc, back pain often occurs in the area of the affected intervertebral disc.
Typical symptoms of a herniated disc
The typical symptoms of a herniated disc include:
Pain
Back pain in the area of the affected intervertebral disc is the most common symptom. If the herniated disc occurs in the lumbar spine, pain may be experienced in the lower back that radiates into the buttocks or right into the legs (sciatica). In the event of a herniated disc in the cervical spine, pain may occur in the neck, shoulders and arms.
Sensory disorders
People with herniated discs may experience numbness or tingling in the areas of the body linked to the affected nerves.
Restricted movement
Mobility may be restricted and people with herniated discs may notice reduced muscle strength in the affected limbs.
Causes of a herniated disc
The intervertebral discs act as a buffer between the individual vertebrae. They allow the spine to move and protect it from impacts and vibrations. Over time or due to disproportionate or excessive strain, they may become damaged. As a result, they increasingly lose their elasticity. Sometimes this can result in soft, gel-like material (intervertebral disc tissue) escaping from the intervertebral disc. This process is referred to as a herniated disc or slipped disc. Herniated discs are most common in the lumbar spine. However, in principle, they can occur in any area of the spine.
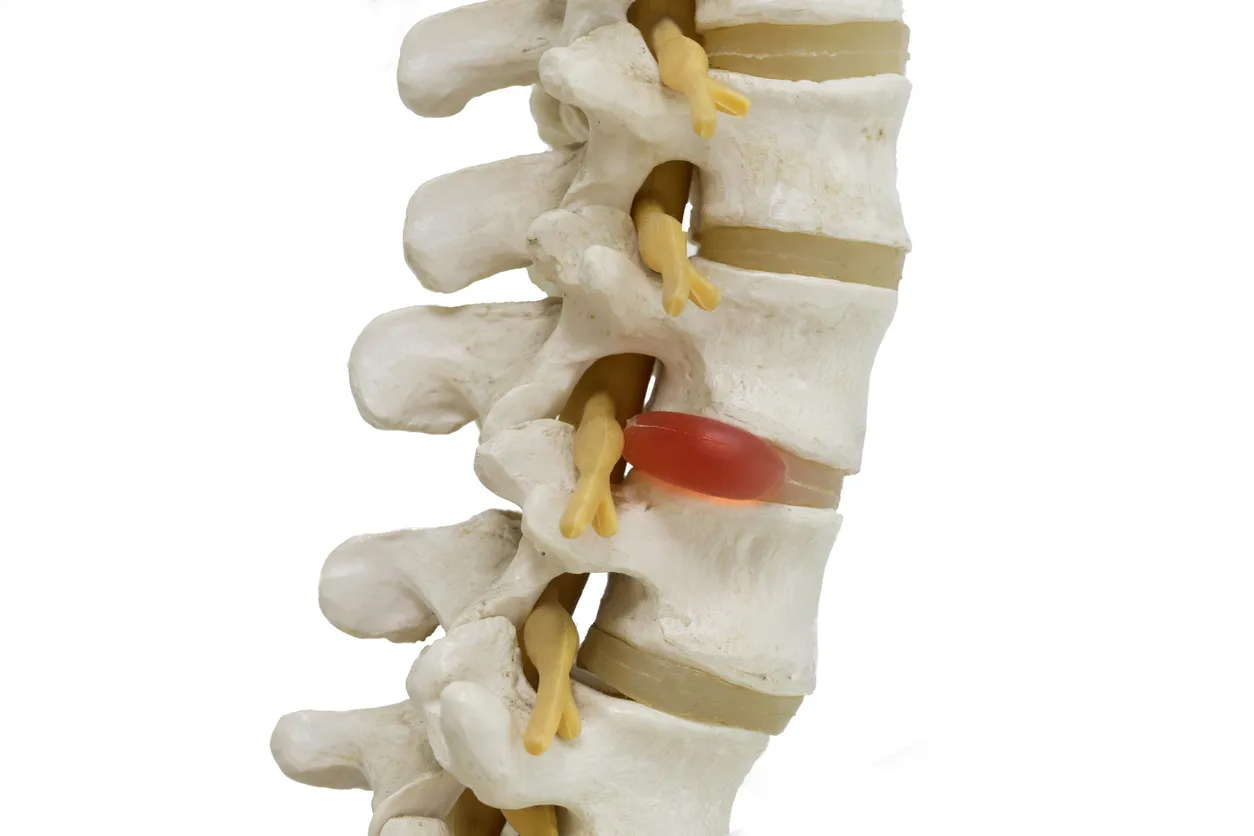
This is how a herniated disc is diagnosed
A herniated disc is diagnosed on the basis of typical complaints and with the help of neurological tests and examinations of the spine. Imaging procedures such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computer tomography (CT) help to identify the exact position and severity of the herniation.
Back Medicine in the Swiss Paraplegic Centre offers you comprehensive and interdisciplinary therapy. Following a referral to Back Medicine, the patient is assessed by specialists in various disciplines in order to make the best possible diagnosis and offer the best possible further treatment. These specialist disciplines include radiology, physiotherapy, pain medicine and back medicine & orthopaedics.
Treatment options
Any treatment option depends on individual factors such as the extent of the herniation, age, health and the patient’s personal preferences. Conservative methods are often recommended first, while surgical interventions may be considered if other treatments are unsuccessful or the symptoms are severe. The majority of herniated discs can be treated effectively with a combination of measures. An operation is required immediately in the case of cauda equina syndrome. This causes a variety of symptoms, including severe pain in the lower back, sensory impairments and paralysis in the legs and in the area of the buttocks, as well as loss of bladder and bowel control.
Procedure in the SPC
The SPC uses a multidisciplinary approach, which allows for individually adjusted treatment for the patient. The team of doctors, physiotherapists, occupational therapists and other specialists carefully assesses each case and prepares a plan tailored to the patient. The emphasis is on comprehensive treatment, which addresses not only the symptoms but also the causes and long-term prevention of back problems. Preference is always given to conservative methods, and invasive interventions are only an option if absolutely necessary and recommended by specialists.
This is how herniated discs are treated
Prevention of a herniated disc
In order to prevent herniated discs, it is important to keep the spine and the surrounding muscles healthy and strong. Here are some effective strategies:
By integrating these preventative strategies into your daily life, you can significantly reduce the risk and frequency of herniated discs. It is always advisable to consult a doctor or a specialist therapist if you have any specific health concerns.

Werden Sie jetzt Mitglied und erhalten Sie im Ernstfall 250 000 Franken.
Spenden Sie jetzt und unterstützen Sie unsere Projekte zugunsten von Querschnittgelähmten.
